Likely Penalties for Drug Supply
What Penalty am I Likely to Receive for my Drug Supply Charge?
In NSW, a court can impose any of the following penalties for a charge of drug supply:
- Section 10 – matter proven but dismissed
- Fine
- Good behaviour bond
- Community Service Order
- Suspended sentence
- Periodic detention
- Home detention
- Prison sentence
You will find a brief description of each of these penalties at the bottom of this page.
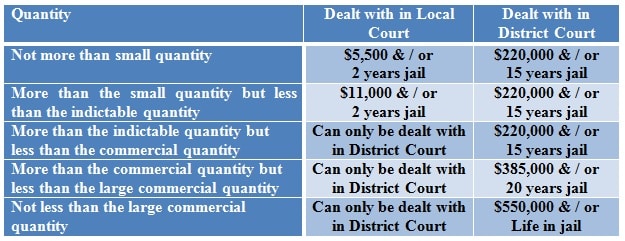
Maximum Penalties for a Drug Supply Charge
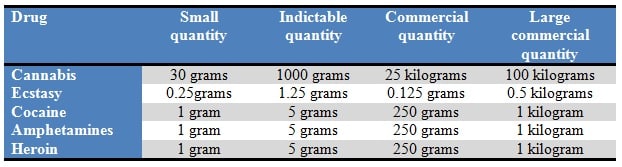
The penalties for supplying drugs increase depending on the quantity of the drug supplied and if the matter is dealt with in the District Court. There are 5 different quantity ranges under the Drug Misuse and Trafficking Act. They are:
- Not more than the small quantity
- More than the small quantity but less than the indictable quantity
- More than the indictable quantity but less than the commercial quantity
- More than the commercial quantity but less than the large commercial quantity
- Not less than the large commercial quantity
The table below outlines the quantity ranges for each of the commonly prosecuted drugs:
The table below outlines the maximum penalty for each quantity:
Sentencing Statistics
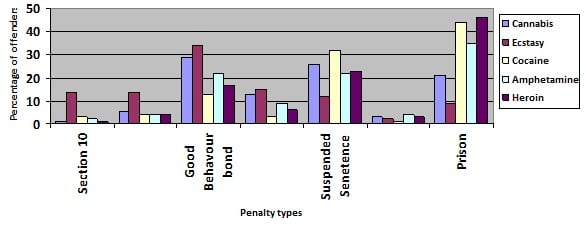
Penalties imposed by the Local Court for all offenders charged with drug supply for the most common drugs (cannabis, ecstasy, cocaine, amphetamines & heroin):
Note the sentencing statistics for home detention was less than 1% for each drug and so was not included.
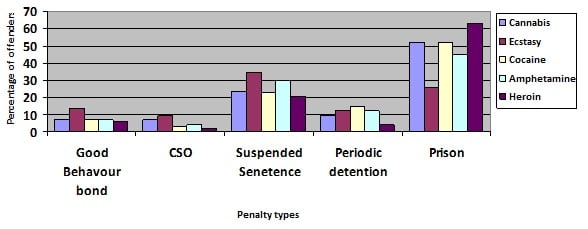
Penalties imposed in the District Court for all offenders charged with drug supply less than the commercial quantity for the most common drugs (cannabis, ecstasy, cocaine, amphetamines & heroin):
Note the sentencing statistics for section 10, fine and home detention were not included because of the low results. It is interesting that 3% of offenders charged with supply ecstasy received a section 10 and 5% of offenders charged with supplying heroin received home detention.
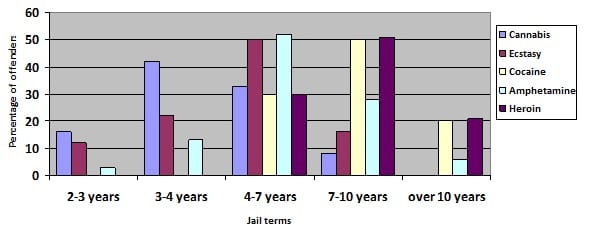
Jail sentences imposed in the District Court for all offenders charged with supplying the commercial quantity of the most common drugs:
Jail sentences imposed in the District Court for all offenders charged with supplying the large commercial quantity of the most common drugs:
Penalties
Common penalties ar outlined below.
Section 10 – avoiding a criminal record
Normally, when you plead guilty to a criminal or traffic offence the Court imposes a penalty and records a conviction. If the court records a conviction you will have a criminal record. However, if we were able to convince the court not to convict you, there would be no penalty of any type and no criminal record. In all criminal cases a court has the discretion not to convict you but deal with you under the terms of section 10.
Fines
By far the most common penalty imposed by the Local Court is a fine. When deciding the amount of any fine the Magistrate or Judge should consider your financial situation and your ability to pay any fine they set.
Good behaviour bonds
A good behaviour bond is an order of the court that requires you to be of good behaviour for a specified period of time. The court will impose conditions that you will have to obey during the term of the good behaviour bond. The maximum duration of a good behaviour bond is 5 years.
Community service order
A Community Service Order (CSO) involves either unpaid work in the community at a place specified by Probation and Parole or attendance at a Centre to undertake a course, such as Anger Management. In order to be eligible for a CSO you have to be assessed by an officer of the Probation service as suitable to undertake the order. Certain medical conditions could exclude you from being suitable to undertake a work order.
Suspended sentence
A suspended sentence (Section 12 good behaviour bond) is a gaol sentence that is suspended upon you entering into a good behaviour bond. Provided the terms of the good behaviour bond are obeyed the gaol sentence will not come into effect. A suspended sentence is only available for sentences of imprisonment of up to 2 years.
Periodic Detention
Periodic detention is a form of imprisonment. It involves detention in a periodic detention centre for a two day period each week for the length of the sentence set by the court. The two-day period commences at 7.00 pm on the day of the week specified (usually Friday) and ends at 4.30 pm on the second day following the day so specified (usually Sunday).
Prison
This is the most severe form of punishment and involves being locked up in a prison. Before a court imposes a prison sentence it must be satisfied that no other penalty other than imprisonment is appropriate.
If you require legal advice or representation in any legal matter, please contact Armstrong Legal.

This article was written by Michelle Makela
Michelle has over 15 years experience in the legal industry, working across commercial litigation, criminal law, family law and estate planning. Michelle has been involved in all practice areas of the firm and in her personal practice has had experience in litigation at all levels (State and Federal Industrial Tribunals, the Supreme Court, Court of Appeal, the Federal Court, Federal...